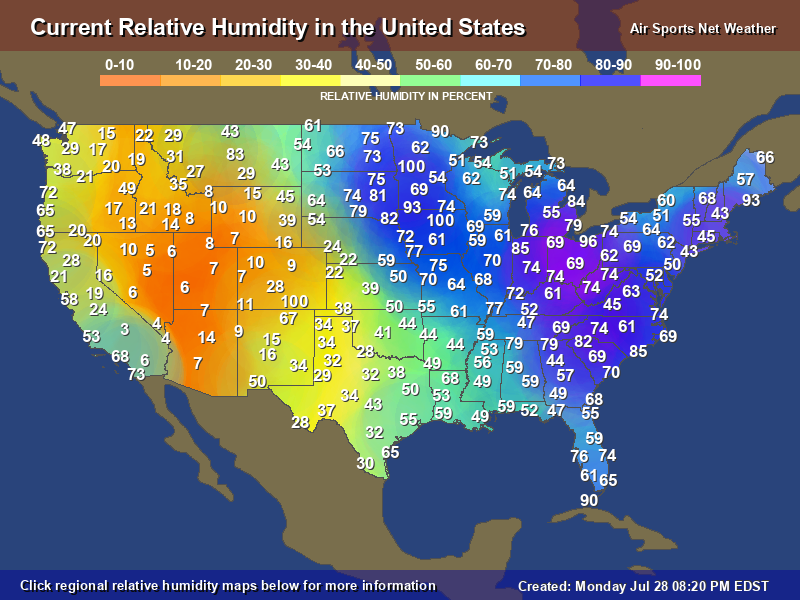
Humidity in the United States is a critical factor influencing weather patterns, human comfort, and overall environmental conditions across the nation. From the humid subtropical climates of the Southeast to the arid deserts of the Southwest, the United States experiences a wide range of humidity levels. Understanding these variations is essential for both meteorologists and everyday citizens who want to adapt to their local climate conditions.
Humidity plays a significant role in shaping daily life, from determining how we dress to influencing agricultural practices. High humidity levels can lead to heat stress, while low humidity can cause dry skin and respiratory issues. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of humidity patterns across the United States, offering insights into how these levels vary by region and their impact on people and ecosystems.
Whether you're a weather enthusiast, a scientist, or simply someone curious about the climate, this guide will equip you with valuable information about humidity in the United States. Let's dive into the details and uncover the complexities of this vital atmospheric component.
Read also:Lawrence Odonnell Wife A Comprehensive Look Into Their Life Together
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Humidity
- Types of Humidity
- Humidity Levels Across U.S. Regions
- Seasonal Variations in Humidity
- Effects of Humidity on Health
- Impact on Agriculture
- Humidity and Climate Change
- Measuring Humidity
- Ways to Reduce Indoor Humidity
- Conclusion
Introduction to Humidity
Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. It is a crucial atmospheric variable that affects weather patterns and human comfort. In the United States, humidity levels vary significantly depending on geographical location, season, and climate type.
Relative humidity is the most commonly used measure of humidity, expressed as a percentage of the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold at a given temperature. High humidity levels often lead to discomfort, especially during summer months, while low humidity can cause dryness and irritation.
Why Humidity Matters
Understanding humidity is important for several reasons:
- It impacts human health by influencing body temperature regulation.
- It affects agricultural productivity by determining moisture availability for crops.
- It plays a role in weather phenomena such as thunderstorms and hurricanes.
Types of Humidity
There are different ways to measure and express humidity, each providing unique insights into atmospheric moisture content:
Absolute Humidity
Absolute humidity measures the total mass of water vapor present in a given volume of air, usually expressed in grams per cubic meter (g/m³). This measurement is less commonly used in daily weather reports but is important for scientific studies.
Relative Humidity
Relative humidity is the ratio of the actual amount of water vapor in the air to the maximum amount it can hold at a specific temperature. It is expressed as a percentage and is widely used in weather forecasts.
Read also:Destroy Core Or Reset Delamain Understanding The Key Concepts And Making The Right Decision
Specific Humidity
Specific humidity refers to the ratio of water vapor mass to the total mass of air, including both dry air and water vapor. This measure is particularly useful in meteorology and atmospheric science.
Humidity Levels Across U.S. Regions
The United States spans a vast area with diverse climates, leading to significant variations in humidity levels across different regions. Below is an overview of how humidity differs in major U.S. regions:
Southeast Region
The Southeast is known for its humid subtropical climate, characterized by hot, muggy summers and mild winters. Cities like Miami, New Orleans, and Atlanta experience some of the highest humidity levels in the country.
Southwest Region
In contrast, the Southwest is predominantly arid and semi-arid, with low humidity levels. States like Arizona and Nevada are famous for their dry desert climates, where relative humidity often drops below 10%.
Midwest Region
The Midwest experiences a mix of humid continental and humid subtropical climates, with moderate to high humidity levels during summer months. This region is prone to thunderstorms due to the combination of heat and moisture.
Seasonal Variations in Humidity
Humidity levels in the United States fluctuate throughout the year, influenced by seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation patterns:
Summer
During summer, humidity tends to be highest, especially in the Southeast and Midwest. This is due to increased evaporation from bodies of water and warm air holding more moisture.
Winter
In winter, humidity levels generally decrease as cooler air holds less moisture. However, coastal areas may still experience relatively high humidity due to proximity to large water bodies.
Spring and Fall
Spring and fall typically have moderate humidity levels, serving as transitional periods between the extremes of summer and winter.
Effects of Humidity on Health
Humidity can have profound effects on human health, both directly and indirectly:
High Humidity
- Increases the risk of heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke.
- Can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma and allergies.
- Leads to discomfort and fatigue due to impaired cooling through sweat evaporation.
Low Humidity
- Causes dry skin, chapped lips, and irritation of the nasal passages.
- Increases the likelihood of respiratory infections by drying out mucous membranes.
- Can damage wooden furniture and musical instruments by causing cracking and warping.
Impact on Agriculture
Humidity plays a critical role in agricultural productivity, influencing crop growth, pest control, and irrigation needs:
Optimal Humidity for Crops
Different crops thrive under varying humidity conditions. For example, tropical fruits like bananas and pineapples require high humidity, while grains like wheat and barley prefer drier conditions.
Pest and Disease Management
High humidity can promote the growth of fungal diseases and pests that harm crops. Farmers often use techniques such as crop rotation and ventilation to mitigate these risks.
Irrigation Strategies
Understanding local humidity levels helps farmers optimize irrigation practices, ensuring that crops receive adequate moisture without wasting water resources.
Humidity and Climate Change
Climate change is altering humidity patterns across the United States, with potential far-reaching consequences:
Increased Evaporation
Warmer temperatures lead to higher evaporation rates, increasing atmospheric moisture content and contributing to more intense precipitation events.
Extreme Weather Events
Rising humidity levels are associated with an increased frequency of severe weather phenomena, including hurricanes, tornadoes, and flash floods.
Regional Disparities
While some regions may experience higher humidity due to climate change, others could become drier, exacerbating drought conditions and water scarcity issues.
Measuring Humidity
Accurate measurement of humidity is essential for weather forecasting, scientific research, and everyday applications:
Hygrometers
Hygrometers are devices used to measure relative humidity. They come in various types, including mechanical, electrical, and digital models.
Psychrometers
Psychrometers use two thermometers—one dry and one wet—to calculate humidity based on the difference in temperature readings.
Satellite and Radar Technology
Modern meteorological tools like satellites and radar systems provide detailed data on humidity levels across large areas, enhancing our understanding of atmospheric processes.
Ways to Reduce Indoor Humidity
Maintaining optimal indoor humidity levels is crucial for comfort and health. Here are some practical tips to reduce excessive indoor humidity:
- Use dehumidifiers to extract excess moisture from the air.
- Ventilate your home by opening windows or using exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms.
- Fix leaks and seal gaps around windows and doors to prevent moisture intrusion.
- Limit activities that generate moisture, such as drying clothes indoors or boiling water without ventilation.
Conclusion
Humidity in the United States is a complex and dynamic phenomenon that significantly impacts weather, health, agriculture, and overall quality of life. By understanding the variations in humidity levels across regions and seasons, we can better adapt to our environment and mitigate the negative effects of extreme humidity.
We encourage you to explore further resources and stay informed about humidity trends in your area. Share this article with others who might find it helpful, and feel free to leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions. Together, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of our atmosphere.