Routing ABA numbers are essential components of the banking system in the United States. They play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth transfer of funds between financial institutions. Understanding what an ABA routing number is and how it works can help individuals and businesses navigate their financial transactions with greater ease and confidence.
For many people, banking transactions may seem like a complex web of numbers and codes. However, once you delve into the specifics, concepts like routing ABA numbers become much clearer. This article aims to demystify the routing ABA number by breaking down its components and explaining its function in the financial ecosystem.
Whether you're transferring funds, setting up direct deposits, or paying bills online, you'll likely encounter the term "routing ABA number." By the end of this article, you'll have a solid understanding of its purpose, how it works, and why it's important in today's digital banking world.
Read also:Judith Harper From Two And A Half Men An Indepth Exploration
Table of Contents
- What is ABA Routing Number?
- History of ABA Routing Numbers
- Structure of an ABA Routing Number
- Types of ABA Routing Numbers
- How ABA Routing Numbers Work
- How to Find Your ABA Routing Number
- Common Uses of Routing ABA Numbers
- ABA Routing Number Security
- ABA Routing vs. SWIFT Codes
- FAQs About ABA Routing Numbers
What is ABA Routing Number?
An ABA routing number, also known as a routing transit number (RTN), is a nine-digit code used by banks and other financial institutions in the United States to identify specific financial institutions within the country. This number is critical for directing funds to the correct bank or credit union during transactions.
The American Bankers Association (ABA) introduced these numbers in 1910 to facilitate the efficient processing of checks. Today, ABA routing numbers are integral to various financial operations, including electronic funds transfers, direct deposits, and automated clearing house (ACH) transactions.
Purpose of ABA Routing Numbers
ABA routing numbers serve several important functions:
- Identify the financial institution responsible for a transaction.
- Ensure that funds are routed to the correct bank or credit union.
- Facilitate both domestic and certain international financial transactions.
History of ABA Routing Numbers
The history of ABA routing numbers dates back to 1910 when the American Bankers Association developed the system to streamline check processing. At the time, the banking industry faced challenges in efficiently processing large volumes of checks. The introduction of routing numbers revolutionized this process by providing a standardized method for identifying financial institutions.
Over the years, the use of ABA routing numbers has expanded beyond checks to include electronic transactions. Today, these numbers are essential for the functioning of modern banking systems.
Read also:Gulf Islands National Seashore Floridamississippi A Paradise Waiting To Be Explored
Evolution of ABA Routing Numbers
As technology advanced, the role of ABA routing numbers evolved:
- Initially used for check processing.
- Adapted for electronic funds transfers and ACH transactions.
- Integrated into digital banking platforms.
Structure of an ABA Routing Number
An ABA routing number consists of nine digits, each with a specific purpose:
- First four digits: Represent the Federal Reserve routing symbol.
- Fifth and sixth digits: Identify the bank's location or region.
- Seventh digit: Indicates the Federal Reserve check processing center assigned to the bank.
- Eighth digit: Denotes the Federal Reserve district where the bank is located.
- Ninth digit: Acts as a checksum to verify the accuracy of the routing number.
Checksum Formula
The checksum formula ensures the validity of an ABA routing number. It involves multiplying specific digits by predetermined weights and summing the results. The final sum must be divisible by 10 for the number to be valid.
Types of ABA Routing Numbers
There are two main types of ABA routing numbers:
- ACH Routing Numbers: Used for electronic transactions, such as direct deposits and bill payments.
- Wire Routing Numbers: Used for domestic and international wire transfers.
While some banks use the same routing number for both ACH and wire transfers, others assign separate numbers for each type of transaction.
Differences Between ACH and Wire Routing Numbers
Understanding the differences between these numbers is crucial:
- ACH routing numbers are generally used for domestic transactions.
- Wire routing numbers may be required for international transfers.
How ABA Routing Numbers Work
ABA routing numbers function as identifiers for financial institutions. When initiating a transaction, the routing number ensures that the funds are directed to the correct bank or credit union. This process is automated and occurs behind the scenes, ensuring swift and accurate processing.
Transaction Process with ABA Routing Numbers
The transaction process involving ABA routing numbers typically includes the following steps:
- Providing the routing number and account information.
- Verifying the details with the financial institution.
- Processing the transaction through the appropriate network.
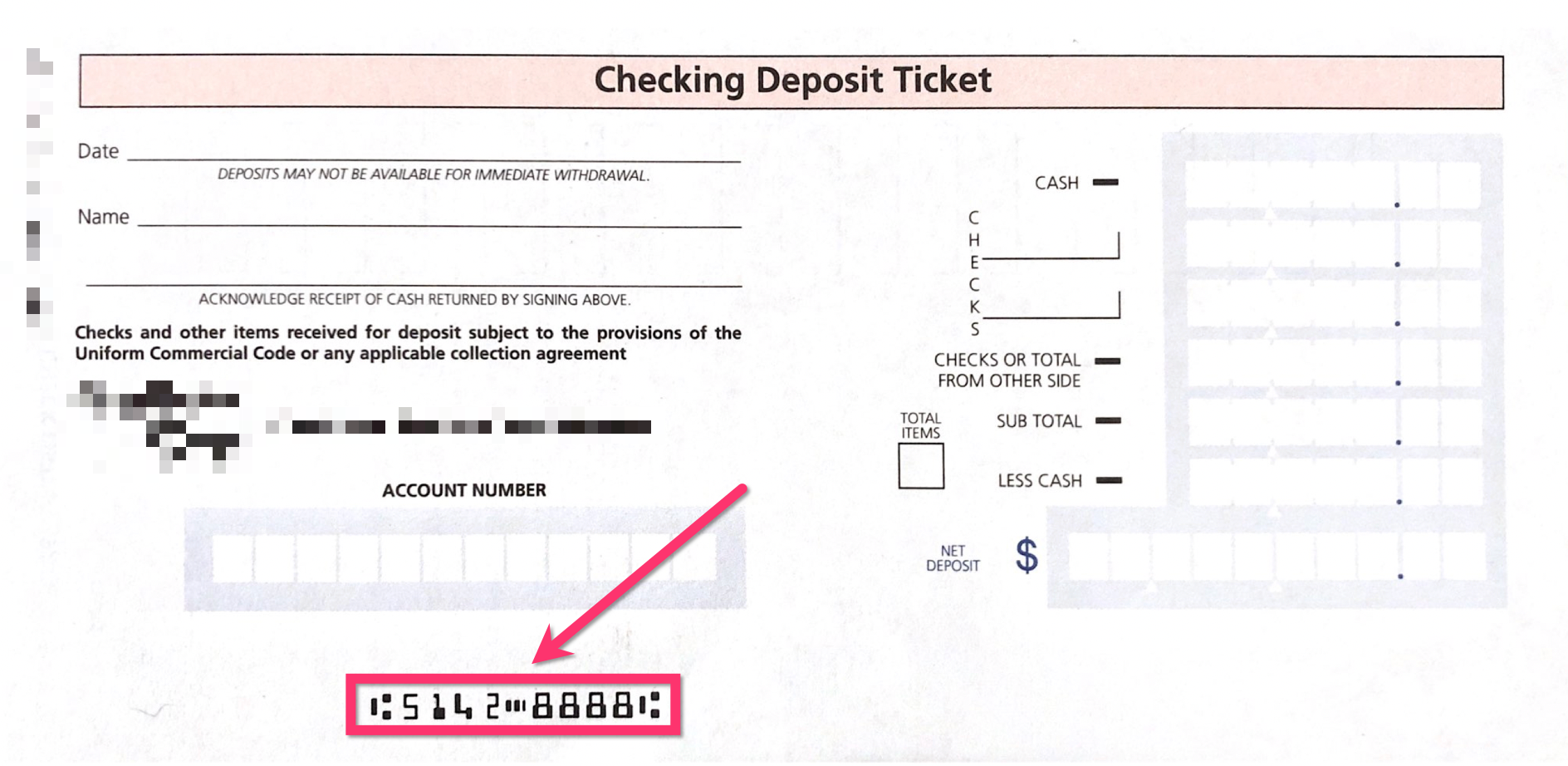
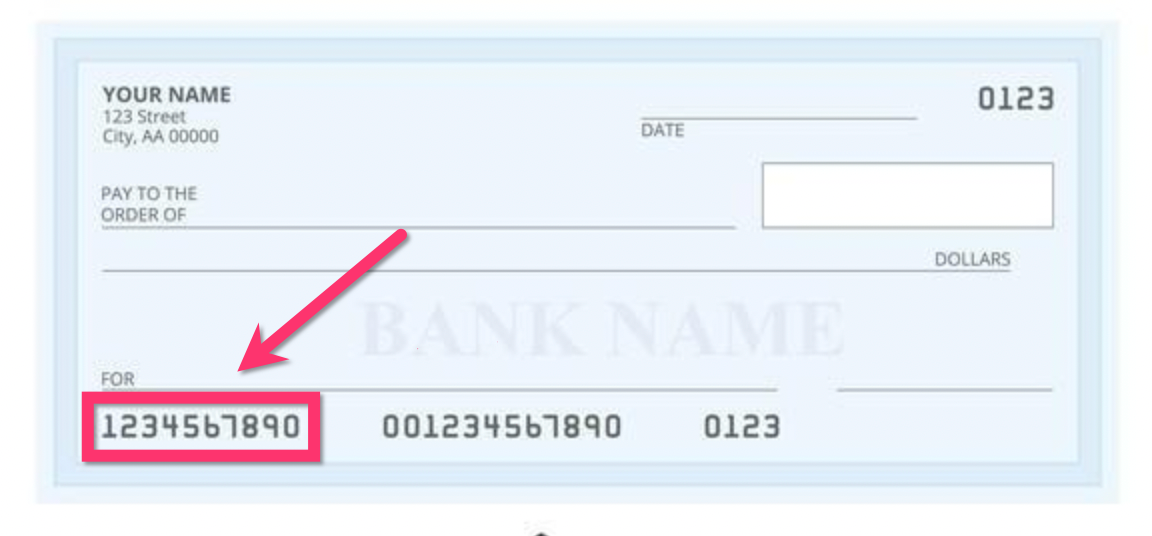
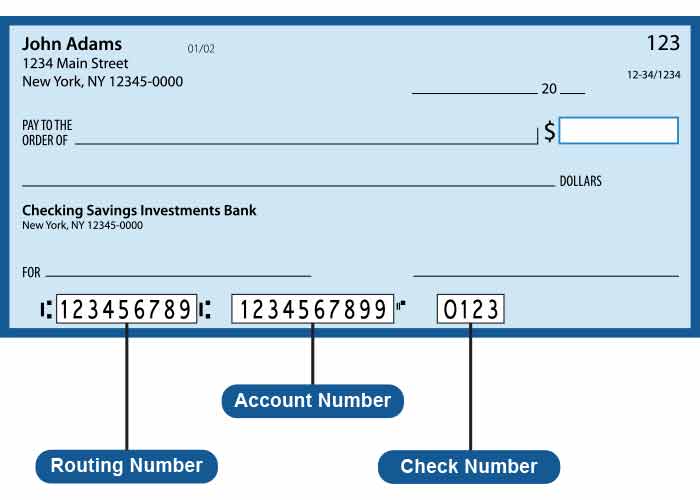
How to Find Your ABA Routing Number
Finding your ABA routing number is straightforward. You can locate it in several ways:
- On Your Checks: The routing number is printed on the bottom-left corner of your checks.
- Online Banking: Access your account information through your bank's website or mobile app.
- Bank Website: Many banks list routing numbers on their official websites.
- Customer Service: Contact your bank's customer service for assistance.
Location of ABA Routing Number on Checks
On personal checks, the ABA routing number is the first set of numbers printed at the bottom. It is followed by your account number and the check number.
Common Uses of Routing ABA Numbers
ABA routing numbers are used in various financial transactions:
- Direct Deposits: Setting up automatic deposits for paychecks or government benefits.
- Bill Payments: Paying bills online or through automated systems.
- Wire Transfers: Sending or receiving funds domestically or internationally.
- ACH Transfers: Transferring funds between accounts electronically.
Examples of ABA Routing Number Transactions
Some common scenarios include:
- Setting up a direct deposit for your salary.
- Paying your utility bills online using your bank account.
- Transferring funds from one bank account to another.
ABA Routing Number Security
Security is a critical aspect of ABA routing numbers. Financial institutions implement various measures to protect sensitive information and prevent fraud. It's important to keep your routing number and account details confidential to avoid unauthorized access.
Tips for Protecting Your ABA Routing Number
Follow these tips to safeguard your information:
- Never share your routing number and account details unnecessarily.
- Use secure networks when accessing your bank account online.
- Monitor your account regularly for suspicious activity.
ABA Routing vs. SWIFT Codes
While ABA routing numbers are used primarily within the United States, SWIFT codes are used for international transactions. Understanding the difference between these two systems is important for global banking.
Key Differences Between ABA Routing and SWIFT Codes
Here are some key distinctions:
- ABA routing numbers are nine-digit codes used domestically in the U.S.
- SWIFT codes are alphanumeric codes used for international transactions.
- ABA routing numbers focus on domestic banking, while SWIFT codes facilitate cross-border transfers.
FAQs About ABA Routing Numbers
Here are some frequently asked questions about ABA routing numbers:
1. Can I use the same ABA routing number for all transactions?
It depends on your bank. Some banks use the same routing number for ACH and wire transfers, while others assign separate numbers for each type of transaction.
2. Is my ABA routing number the same as my account number?
No, your ABA routing number identifies your bank, while your account number identifies your specific account within that bank.
3. Can I find my ABA routing number online?
Yes, most banks provide routing numbers on their official websites. You can also find it on your checks or through online banking.
4. What should I do if I suspect fraud involving my ABA routing number?
Contact your bank immediately to report the issue and take steps to protect your account.
5. Are ABA routing numbers used outside the U.S.?
ABA routing numbers are primarily used within the United States. For international transactions, SWIFT codes are typically required.
Kesimpulan
In conclusion, understanding what an ABA routing number is and how it functions is essential for managing financial transactions effectively. From facilitating direct deposits to enabling wire transfers, ABA routing numbers play a vital role in the banking system. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure the security and accuracy of your financial transactions.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from understanding ABA routing numbers. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to leave a comment below. For more informative content on banking and finance, explore our other articles on the site.
References: